You are here: Books --> Effective Onscreen Editing 4th edition --> Word 2016 Chapter 3: Personalizing Your Software
Vous êtes ici : Livres --> Effective Onscreen Editing 4th edition --> Word 2016 Chapter 3: Personalizing Your Software
Chapter 3: Personalizing Your Software
“The reasonable man adapts himself to the world; the unreasonable one persists to adapt the world to himself. Therefore all progress depends on the unreasonable man.”—George Bernard Shaw (1856–1950)
Software and reference links for all versions of Word
This Web page contains instructions on the following subjects:
Adding or modifying toolbars (Word 2010)
Arranging window positions (tiling windows)
Changing display settings
Choosing the keyboard layout (adding a keyboard)
Changing a window's size
Customizing keyboard shortcuts
Customizing the Quick Access toolbar
Customizing the Ribbon
Displaying the Styles palette
Document map (navigation pane) view
Dynamic style guides
Finding the control panels and settings
Keyboard settings
Macro for turning off the Asian grid setting
Mouse settings
Navigating menus from the keyboard
Navigation pane (document map) view
Outline view (an example)
Splitting a window into two panes
Switching windows from the Ribbon
Using a CRT monitor
Adding or modifying toolbars (Word 2010)
In Word 2010 for Windows, you still had some control over toolbars. For details of the changes you can make in these toolbars, download (PDF) the document Adding or modifying toolbars.
In Word 2016, you can only modify the Quick Access toolbar. The Quick Access toolbar is located at the top of Word's interface, above the ribbon:
To reposition this toolbar, click the downward-pointing arrow to display a menu of options, then select Show Below the Ribbon:
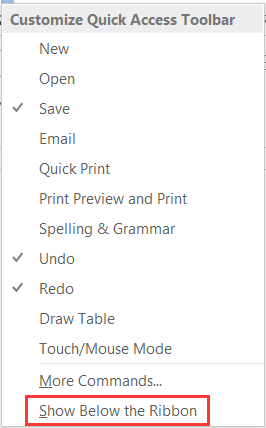
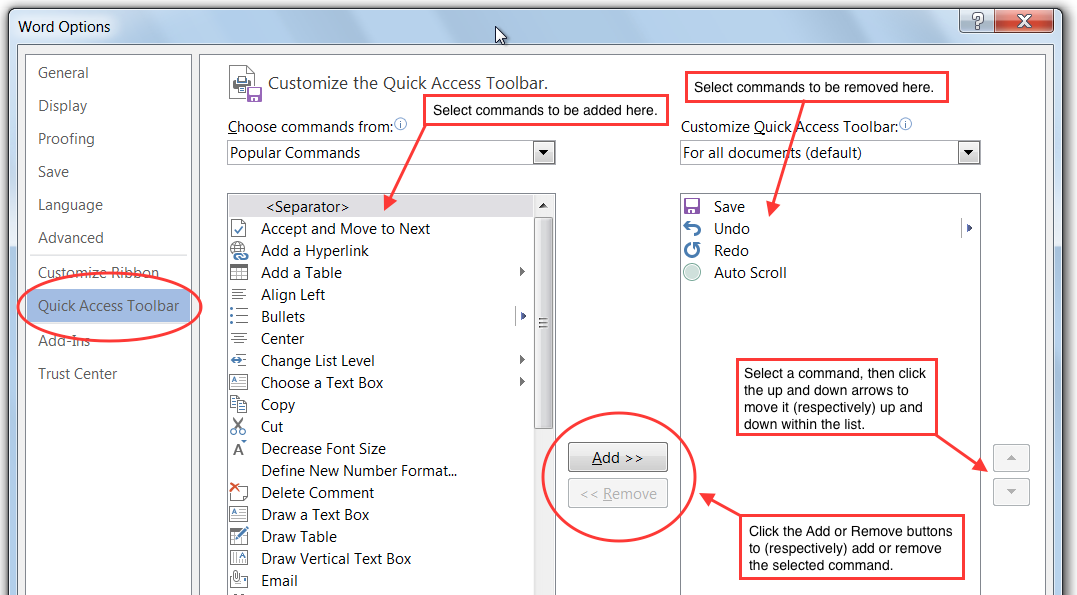
To add or remove icons from the toolbar, display the Options dialog box (as described above), then select the Quick Access Toolbar tab. From this tab, you can select commands to be added to or removed from the toolbar, and you can change their positions within the toolbar:
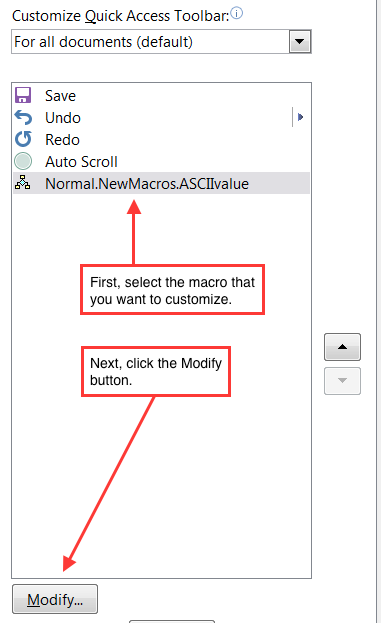
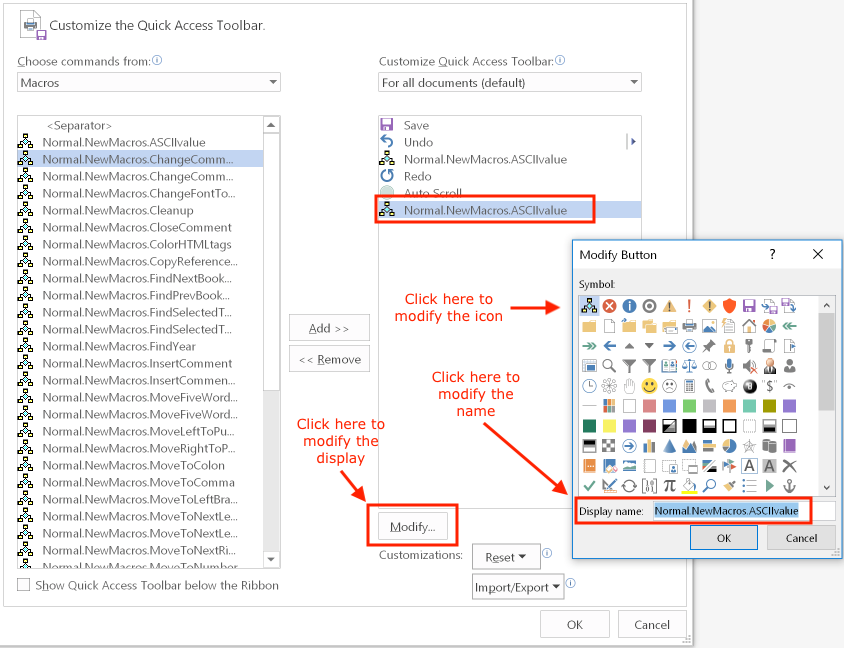
To change the icon or choose a new tooltip for any item in the toolbar, select that item and then click the Modify button. For example, for a macro:
Arranging window positions (tiling windows)
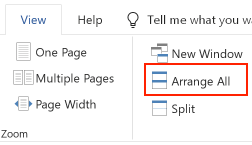
To automatically divide the screen among multiple windows, open the Window menu and select Arrange All:
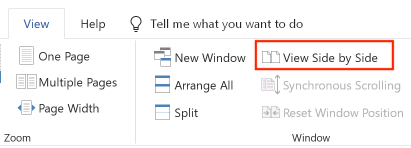
You can instead use the "View Side by Side" option:
Changing display settings
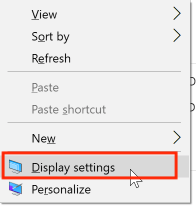
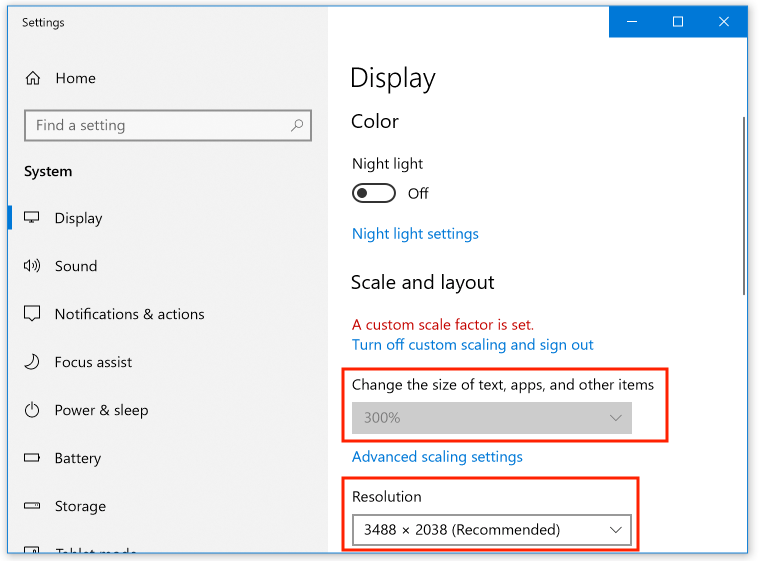
To adjust the Display settings, click to select the Windows desktop, then press the Windows key. From the menu, select Display Settings:
From this dialog box, yoiu can adjust the text and icon size and the display resolution:
To select or deselect Microsoft's pixel smoothing options ("ClearType antialiasing"), click to select the Windows desktop, then press the Windows key. From the menu, select Personalize:
 :
:
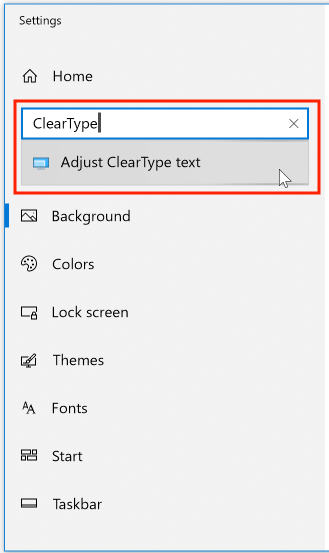
In the search field, type "ClearType", and then click the link for "Adjust ClearType text":
Follow the instructions in the ensuing sequence of dialog boxes.
Choosing the keyboard layout (adding a keyboard)
Open the Taskbar, select the Windows icon, then select settings:
Select "Time and Language" group of settings:
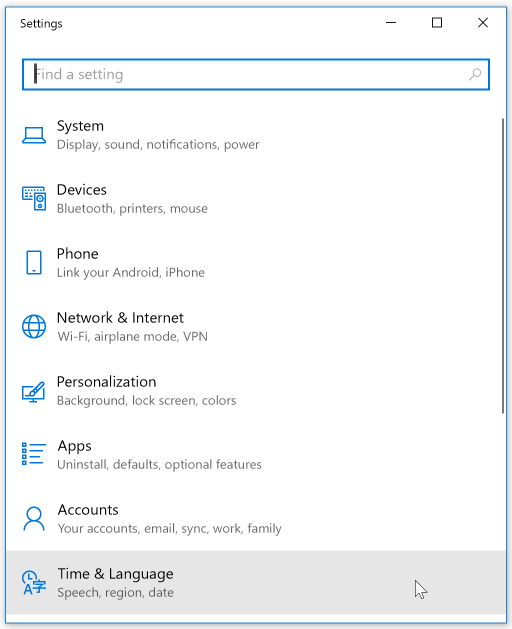
Click the “Region and language” link
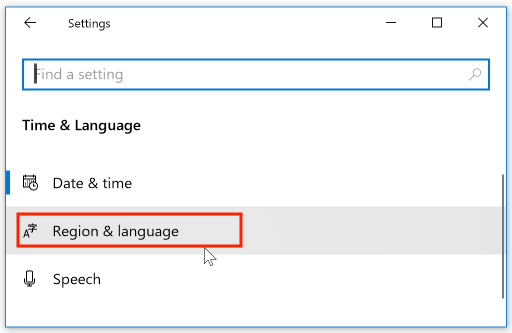
Select the language for which you want to add a keyboard, then click the Options button:
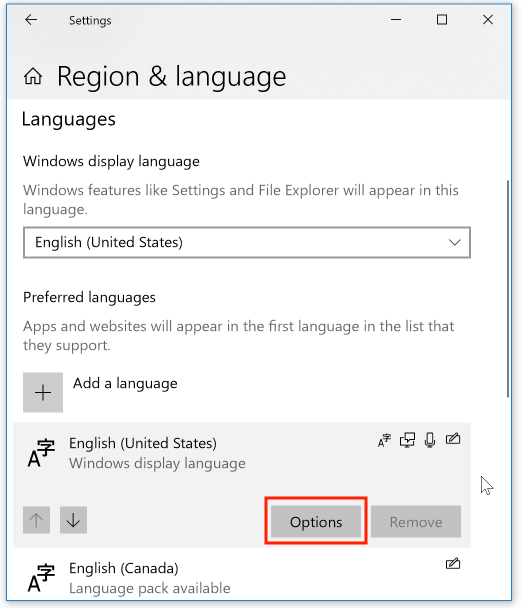
Click the “Add a keyboard” option to gain access to additional keyboard layouts:
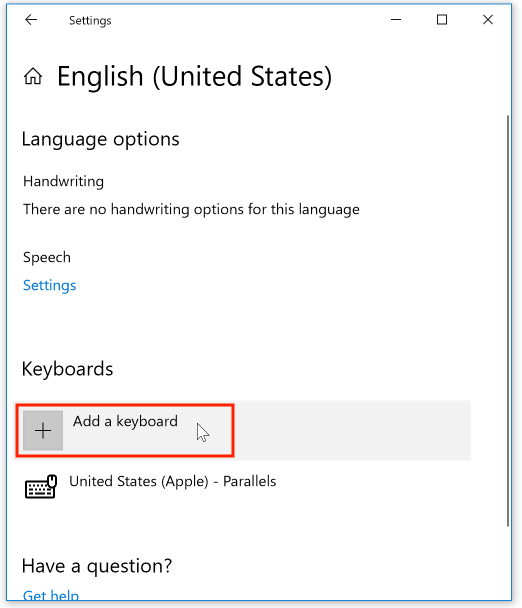
Note that the menu below the "Add a keyboard" option displays all currently installed keyboards, and lets you choose which of the available keyboards to use.
Select the new keyboard that you want to make available (e.g., Canadian French) then click "OK". To define a keyboard shortcut to switch between keyboard layouts, open the "Region and Language" control panel (as described earlier in this topic), and then scroll down to "Advanced Keyboard Settings":
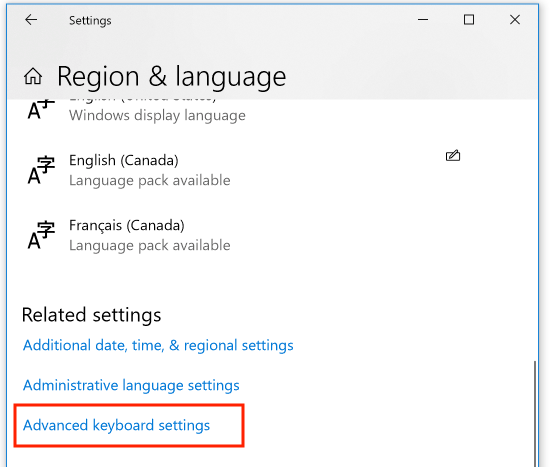
Click the "Options" button:

Select the "Advanced Key Settings" tab, select "Between input languages", and then click "Change Key Sequence" and choose a new shortcut:
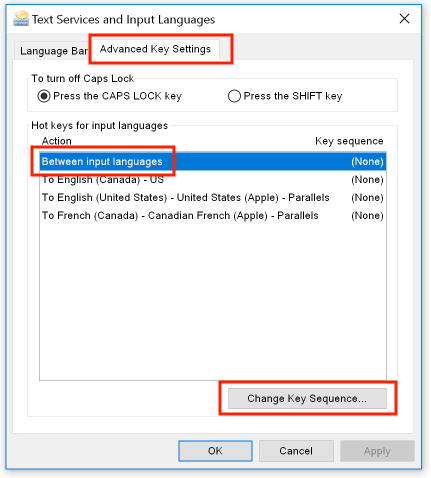
Define a keyboard shortcut that will let you make this change without having to go through this endless sequence of dialog boxes.
Changing a window's size
To change the window's size, move the mouse cursor over the edge of the window until it changes to a double-headed arrow (here, shown at the bottom right corner of a document window):
Hold down the left mouse button, and drag the window until it's the desired size. You can resize windows this way and then drag them into new positions.
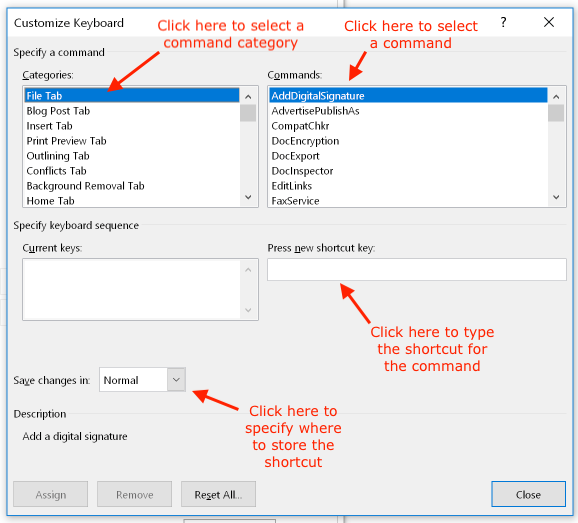
Customizing keyboard shortcuts
To access the dialog box that lets you create and modify keyboard shortcuts, open the "File" menu, select "Options", and then select the "Customize Ribbon" tab. At the bottom of the dialog box, click the button "Customize" beside the heading "Keyboard shortcuts":
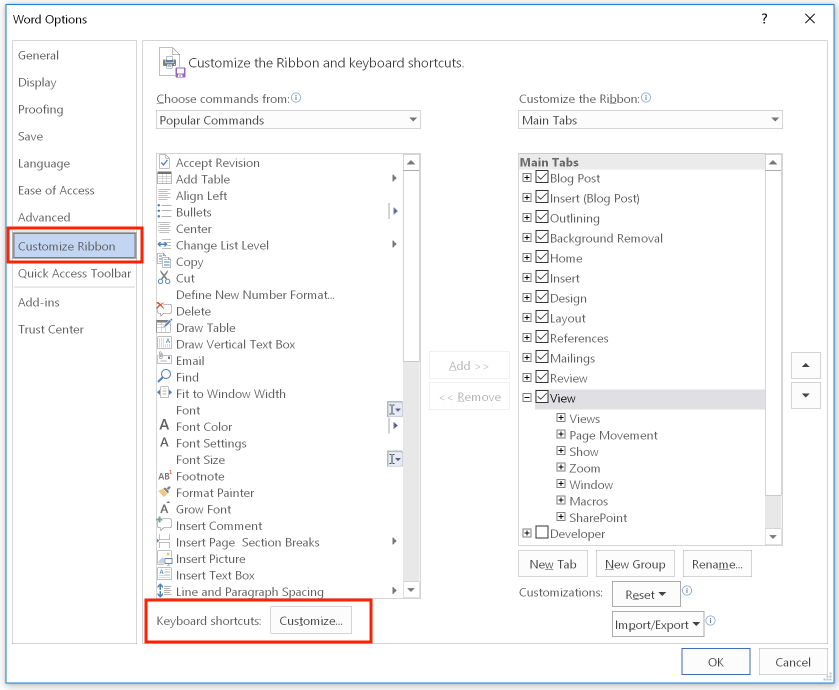
In the "Customize Keyboard" dialog box, select the category of command and the command for which you want to define a new keyboard shortcut. Word shows you existing keystrokes for that command, and warns you if you chose a keystroke that is already assigned to a different command. (You can make this change if you don't use that keystroke for the other command.) Next, choose where to store the new shortcut. Finally, click the Assign button to implement your change:
Customizing the Quick Access toolbar
The QuickAccess toolbar is located at the top of Word's interface, above the ribbon:
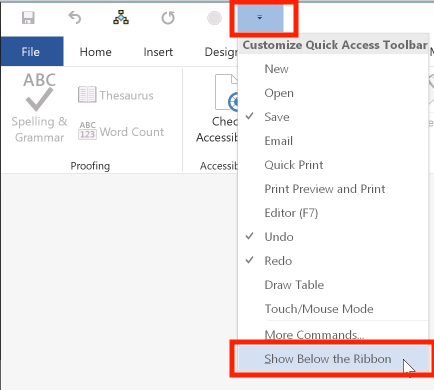
To reposition this toolbar, click the downward-pointing arrow to display a menu of options, then select Show Below the Ribbon:
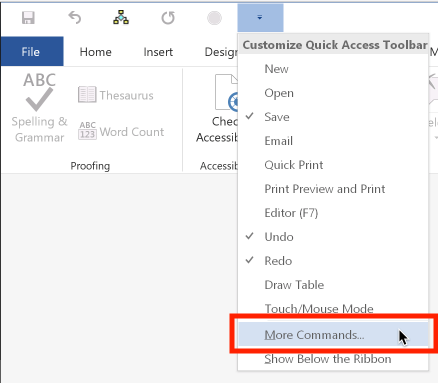
To add icons to or remove icons from the toolbar, select "More commands":
To add or remove icons from the toolbar, or change the icon or tooltip for an item in the toolbar (but not for most built-in commands), select the command name and then click the Modify button:
Customizing the Ribbon
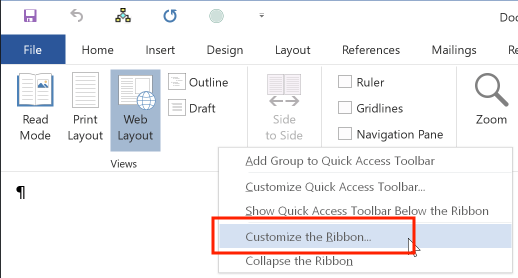
To customize the Ribbon, right-click anywhere in the ribbon to display a contextual menu, and select "Customize the Ribbon":
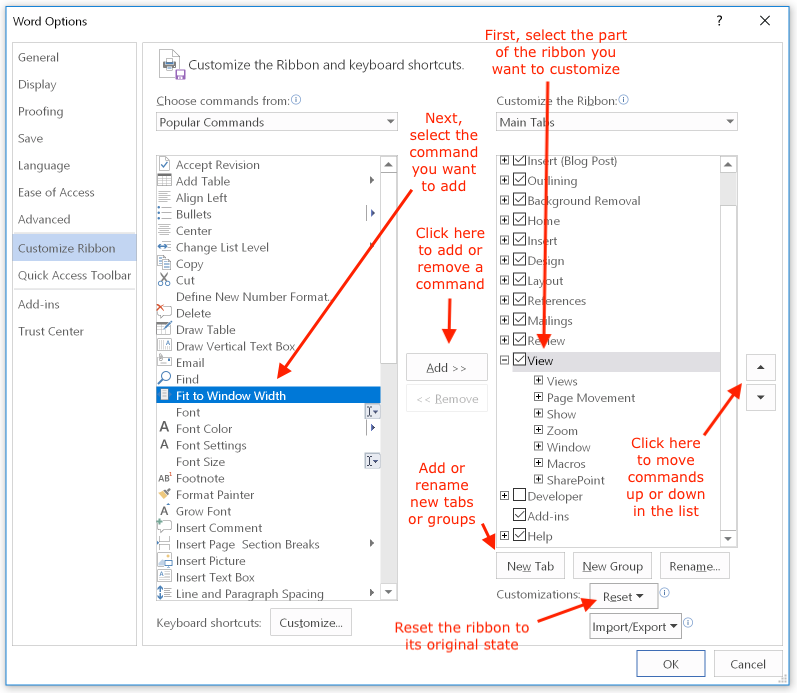
To add commands to or remove them from the Ribbon, start by selecting the tab (here, "View") and group that you will modify. Click the "Add" button to add the command to the Ribbon, or the "Remove" button to remove the command. You can use the arrows to change a command's position within its group, and you can create and rename tabs and groups:
Displaying the Styles palette
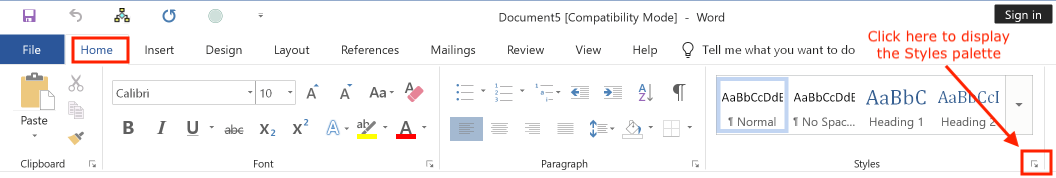
To display the Styles palette from the Ribbon, select the "Home" tab and click the small menu icon at the bottom of the "Styles" group of icons:
The Styles palette lets you apply styles by selecting text and clicking the style name to apply it to that text. Note the different notations for paragraph (¶) and character (a) styles. Also note that by default, only styles currently in use in the document will be listed:
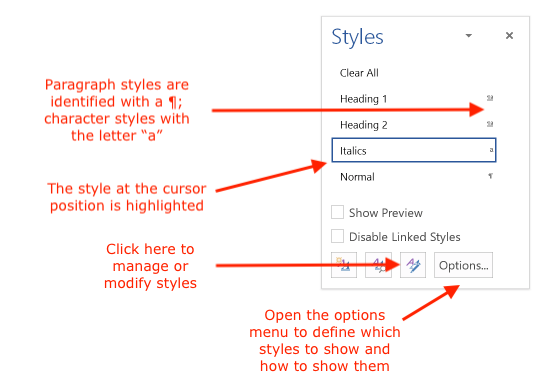
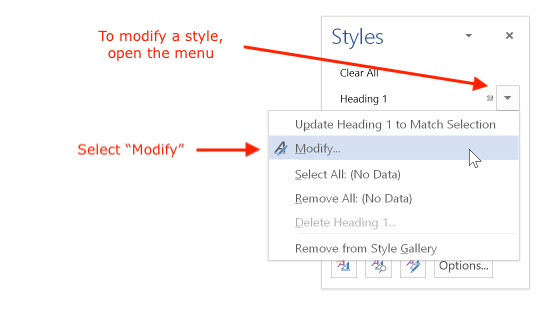
To modify the properties of a style, open the menu beside the style name and select "Modify":
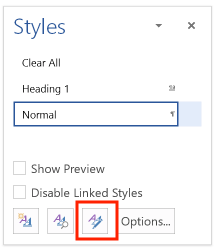
Alternatively, click the "Manage styles" button:
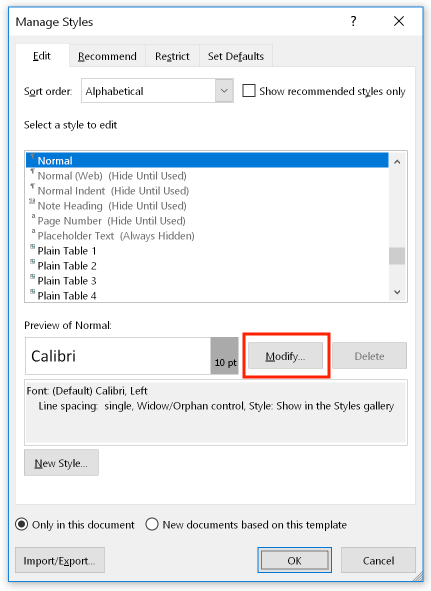
In the "Manage Styles" dialog box, select the style you want to modify and click the "Modify" button to gain access to its properties:
Dynamic style guides
The purpose of creating a dynamic style guide is to integrate the style guidance with how writers and editors work. For a discussion of how this might work, see The style guide is dead: long live the dynamic style guide.
Finding the control panels and settings
The location of the control panels depends on where you've set Windows to display the Taskbar. I've chosen the left side of the screen. To display the Taskbar, move the mouse cursor to the edge of the screen that holds the Taskbar. Next, click the Windows icon and scroll down to "Control Panels" or "Settings" in this sub-menu:
Keyboard settings
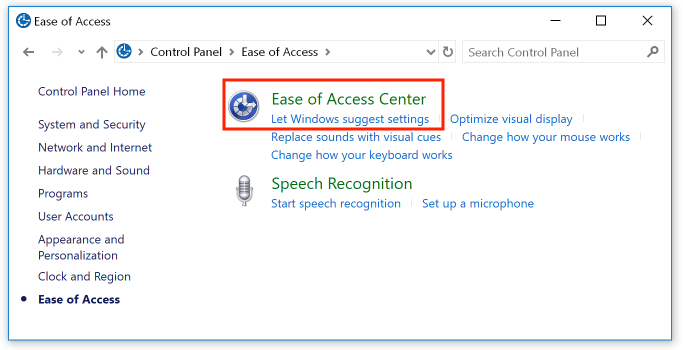
Display the Control Panels (see the previous topic on this page for details), then select "Ease of Access". From the available options below this heading, select "Change how your keyboard works":
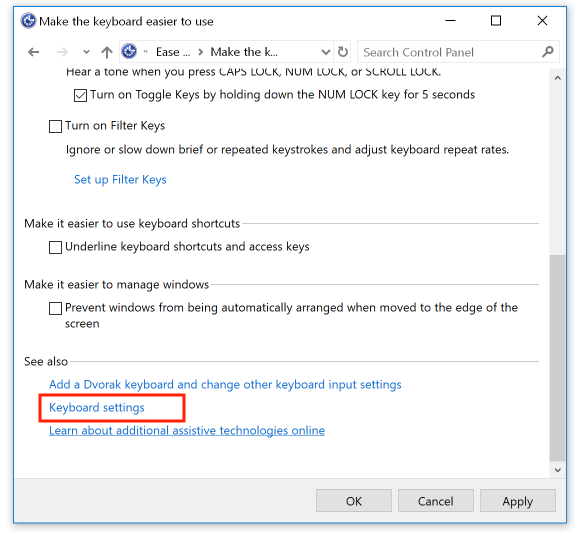
Scroll down to the bottom of the dialog box and select "Keyboard settings":
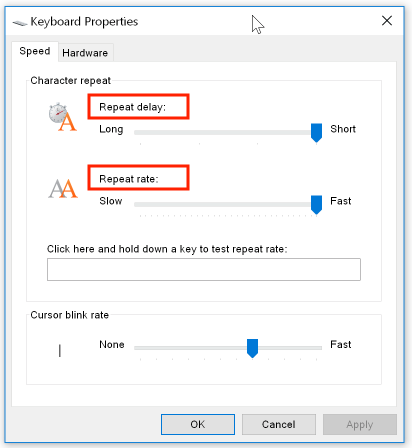
Choose a keyboard repeat rate and delay:
Navigation pane (document map) view
First, select the Ribbon's View tab, choose a view from the "Views" group, and then select the "Navigation Pane" checkbox:
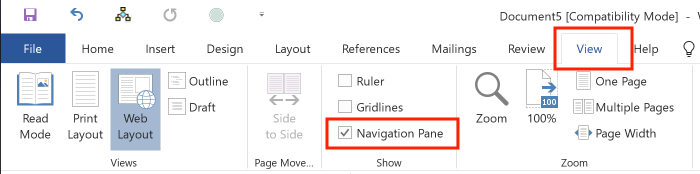
The navigation pane looks like this:
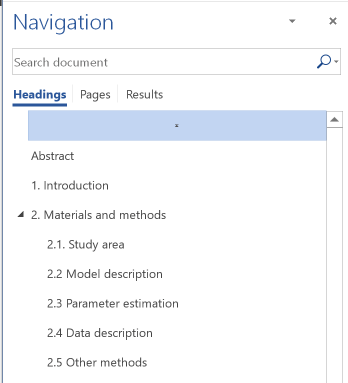
Click any heading to move to that heading.
Macro for turning off the Asian grid setting
See Chapter 10 for details of how to copy this text into a new macro.
Sub TurnOffGrid2()
' TurnOffGrid2 Macro
ActiveDocument.PageSetup.LayoutMode = wdLayoutModeDefault
End Sub
Mouse settings
Display the Control Panels, as described earlier on this page, and choose the "Ease of Access" group of options. From the available options, choose "Change how your mouse works":
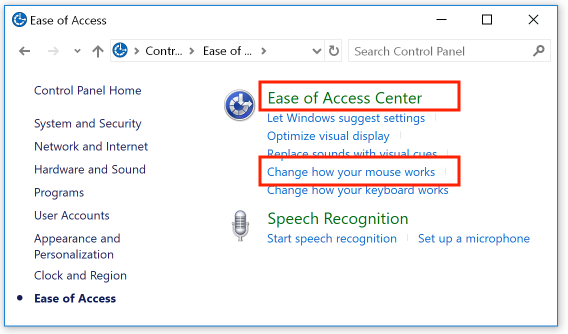
Scroll down and click the link to the "Mouse settings" options:
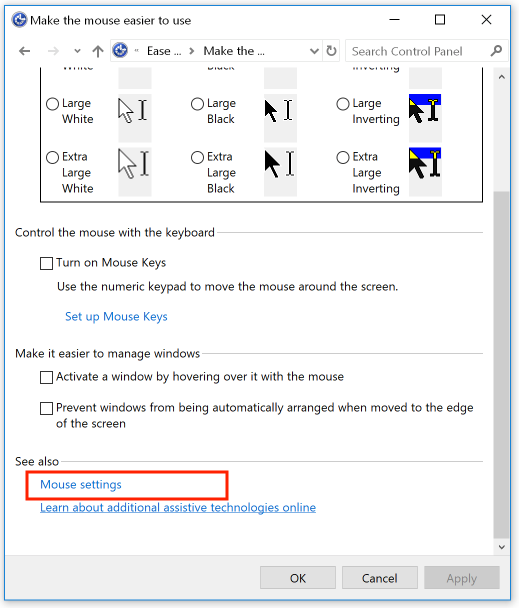
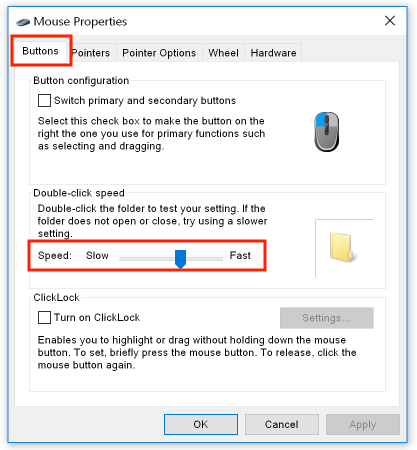
In the "Buttons" tab, adjust the double-click speed:
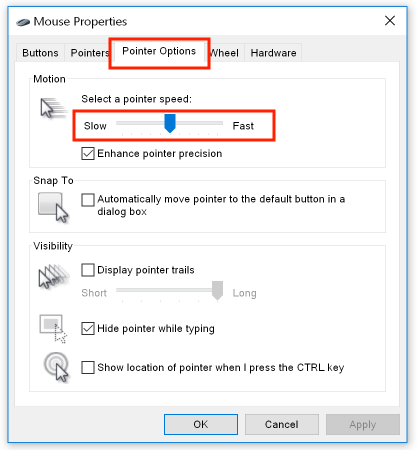
In the "Pointer Options" tab, select the tracking speed:
Navigating menus from the keyboard
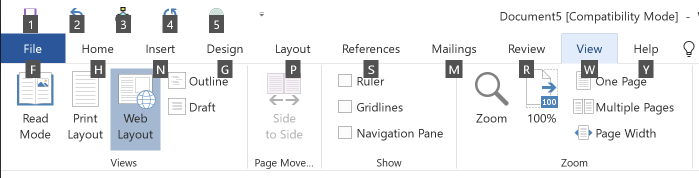
To navigate menus from the keyboard, start by pressing the Alt key. Letters will appear beside the name of each tab in the Ribbon, allowing you to select that tab by pressing the corresponding letter. Note that the six items in the Quick Access toolbar are numbered rather than labeled with letters:
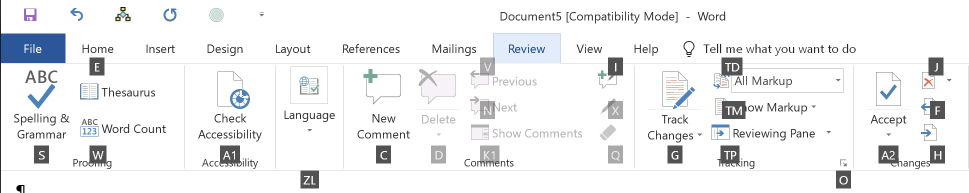
For example, to move to the "Review" tab, simply press R, thereby revealing shortcut letters for all commands that are available via the "Review" tab. To access a specific command, press its letter or letters. For example, to open the Show Markup menu, press T, then M:
Each additional item in a menu can be accessed by typing its own associated keystroke.
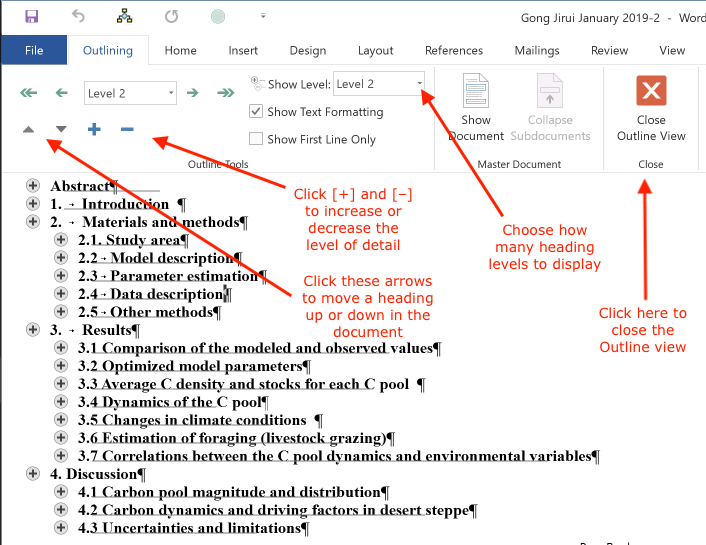
Outline view (an example)
Here's what a document looks like in Outline view, with only heading levels 1 and 2 showing:
Splitting a window into two panes
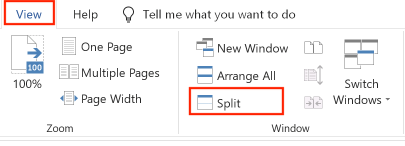
To split a window into two panes, select the Ribbon's View tab and click the "Split" icon:
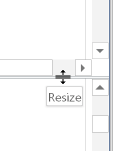
Note that the icon changes to "Remove split", so you can click that icon to restore a single pane. If you hold the mouse cursor over the line that marks the boundary between the top and bottom panes of the window, the cursor will change in to a double-headed arrow. Drag the cursor until you achieve the desired balance between the two panes:
Switching windows from the Ribbon
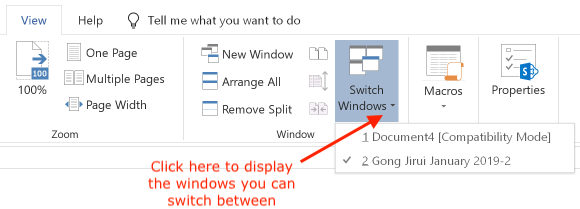
To switch windows from the Ribbon, select the "View" tab, click the "Switch Windows" icon, and then select the desired window from the resulting menu:
Using a CRT monitor
Most editors now use an LCD monitor. If you're still using a CRT monitor, download Working with CRT monitors (PDF) for some tips.
©2004–2025 Geoffrey Hart. All rights reserved.




![]()




 :
:


































